Welcome to Saim Tech Blog! Today, we’ll dive into the heating air technicaly systems. Maintaining a comfortable indoor space is essential, and an efficient HVAC system plays a crucial role in achieving this. This guide will cover the basics of HVAC systems and explain how they manage temperature, humidity, and air quality in your space. HVAC systems work to regulate the thermal environment by adjusting temperature, airflow, and humidity, ensuring that your indoor climate remains comfortable regardless of outside conditions. Understanding how these systems work will help you make better choices for the comfort of your home or building.
Key Takeaways
- Heating ventilation and air conditioning systems are used in buildings to provide comfort to people inside buildings.
- Understanding the technical aspects of HVAC systems can help you make informed decisions about your home or building’s thermal management.
- HVAC systems manipulate temperature, airflow, and humidity levels to create a customized indoor climate.
- Familiarizing yourself with the basic components and the science behind HVAC technology can enhance your understanding of these systems.
- This guide provides a comprehensive introduction to the fundamentals of HVAC systems, covering their key elements and the principles that govern their operation.
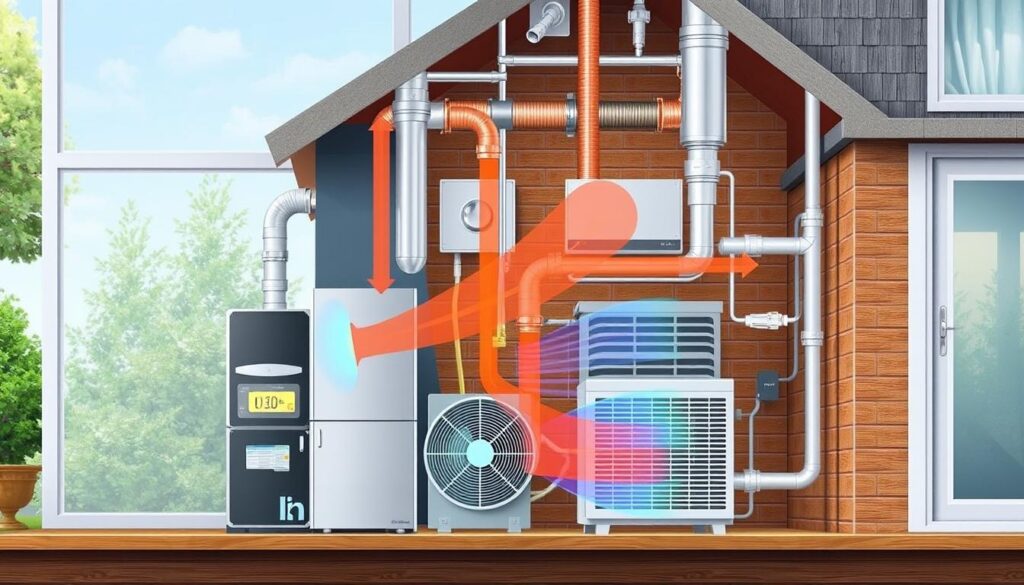
What Makes Up a Modern HVAC System
Knowing the parts of a modern HVAC system is key for homeowners and building managers. These systems keep your space comfortable, save energy, and improve air quality. Let’s look at the main parts of a top-notch HVAC system.
Primary Components and Their Functions
The main parts of an HVAC system are the furnace, air conditioner, heat pump, and air handler. The furnace warms the air, while the air conditioner cools and dries it. The heat pump does both heating and cooling, moving heat in or out as needed. The air handler spreads the cooled air through ducts and rooms.
Integration of System Elements
The main HVAC parts work together for a complete climate control solution. The furnace and air conditioner, or heat pump, connect to the air handler. This spreads the treated air through ducts. Refrigerant lines link the outdoor unit to the indoor handler, for heat transfer.
Control Mechanisms and Automation
Modern HVAC systems have advanced controls and automation for better efficiency and ease. Programmable thermostats let you set temperatures and control remotely. Built-in sensors adjust the system based on indoor conditions. Automated zoning and smart home integration let you control the system with voice commands or apps.
Knowing about modern HVAC systems helps you make smart choices for your climate control. This knowledge lets you create a comfortable, energy-saving, and well-ventilated space that meets your needs.
| HVAC Component | Primary Function | Key Features |
| Furnace | Generates warm air | Fuel-powered (gas or electric), high-efficiency models available |
| Air Conditioner | Cools and dehumidifies air | Outdoor compressor unit, indoor air handler, refrigerant lines |
| Heat Pump | Provides both heating and cooling | Reversible refrigerant cycle, efficient in moderate climates |
| Air Handler | Circulates conditioned air | Blower fan, air filters, ductwork connections |
Understanding modern hvac systems helps you improve your indoor environment’s performance, efficiency, and comfort. Whether upgrading or designing a new air conditioning setup, this knowledge helps you make informed choices for your ventilation systems.
The Science Behind Heating Air Technicaly
Understanding how HVAC systems heat air is key for comfort and saving energy. At the core are thermodynamics and heat transfer. These principles control how air interacts with its surroundings.
Heating air technically means changing its temperature and humidity. This involves complex heat exchange. It includes conduction, convection, and radiation.
HVAC systems manage heat through transfer. Energy moves from hot to cold areas. This follows the laws of thermodynamics.
To heat air well, HVAC systems use many parts. Heat exchangers, compressors, and fans work together. Advanced controls and automation help manage air temperature, humidity, and flow. This makes indoor spaces comfortable and energy-saving.
| Principle | Description |
| Conduction | The transfer of heat through physical contact, such as when a warm object is in direct contact with a cooler one. |
| Convection | The transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid, such as air or water, carrying heat from one location to another. |
| Radiation | The heat transfer that does not require any distinct material or direct contact between the two objects. |
Knowing the science of heating air technically helps HVAC experts. They can create systems that manage temperature, humidity, and airflow. This ensures comfortable and energy-efficient spaces for everyone.
Essential Principles of Heat Exchange
Knowing the basics of heat exchange is key for making HVAC systems work well. In heating and cooling, conduction, convection, and radiation are crucial. Let’s dive into these important ideas.
Conduction and Convection Basics
Conduction happens when materials with different temperatures touch each other. Heat moves from the warmer to the cooler side. Convection, on the other hand, moves heat through fluids like air or water. This is important for HVAC systems to spread cooled or heated air around.
Radiation and Heat Transfer Methods
Radiation moves heat through waves, even without touching anything. This is key in heat exchange. Knowing how conduction, convection, and radiation work helps improve thermal management and energy efficiency in HVAC systems.
Temperature Differential Effects
The difference in temperature between two things drives heat exchange. The bigger the difference, the quicker the heat moves. This idea is at the heart of HVAC design and operation, aiming to control temperatures efficiently.
| Heat Exchange Principle | Description | Relevance to HVAC |
| Conduction | Heat exchange that takes place from one body to the next without the use of an intermediate medium. | Governs heat flow within solid components of HVAC systems, such as heat exchangers and ductwork. |
| Convection | The actual moving of heat through the use of fluids, either in the form of air or water vollume. | Facilitates the distribution of conditioned air throughout a building and the heat exchange process in HVAC equipment. |
| Radiation | Transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, allowing heat to travel without a physical medium. | Influences the absorption, emission, and reflection of thermal energy in HVAC systems, impacting overall energy efficiency. |
Understanding heat exchange basics helps HVAC experts design better systems. These systems manage thermal management and boost energy efficiency in buildings.
Understanding Air Distribution Systems
Efficient air distribution is key in modern HVAC systems. Proper duct design and airflow management are crucial. They help keep indoor air quality and temperature consistent. Knowing about ventilation systems can make your HVAC more efficient and save energy.
Ductwork design is a big deal in air distribution. Ducts carry conditioned air to different rooms. The duct’s size, shape, and layout affect airflow, pressure, and temperature in the building.
Fans and blowers are vital in air distribution. They create airflow to move conditioned air through ducts and into rooms. Properly placed and sized fans ensure air circulates evenly. This prevents hot or cold spots and keeps the environment comfortable.
| Key Factors in Air Distribution | Importance |
| Duct Design | Ensures efficient airflow and temperature control |
| Fan and Blower Placement | Facilitates even air circulation throughout the building |
| Airflow Patterns | Maintains consistent indoor air quality and comfort levels |
Understanding air distribution can improve your HVAC system’s performance. It also boosts indoor air quality and energy efficiency. This makes your building more comfortable and efficient.
Refrigeration Cycles in HVAC Operations
The refrigeration cycle is key to modern air conditioning and heat pumps. It efficiently moves heat, making HVAC systems work well. Knowing how refrigeration cycles work helps us make our HVAC systems better and more energy-efficient.
Compression and Expansion Processes
In carrying out the refrigeration cycle, the spirit of the system is the compressor. It uses electricity to pressurize the refrigerant, making it hot. This hot, high-pressure refrigerant then goes through the condenser, where it loses heat to the air or water.
As it cools, the refrigerant expands and becomes a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid. This liquid then goes through the evaporator. There, it absorbs heat from the air inside, cooling it down.
Refrigerant Types and Properties
The refrigerant used in HVAC systems affects their energy use and the environment. Old refrigerants like CFCs and HCFCs harmed the ozone layer. Now, HVAC systems use safer refrigerants like HFCs and HFOs, which are better for the planet and more energy-efficient.
System Efficiency Factors
Many things affect how well an HVAC system works. These include the system’s design, the refrigerant’s quality, and the environment. Keeping the system well-maintained and using energy-saving features can make it more efficient and cut costs.
| Refrigerant Type | Global Warming Potential (GWP) | Energy Efficiency |
| Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) | High | Moderate |
| Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) | Moderate | Moderate |
| Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) | Low | High |
| Hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) | Very Low | Very High |
Ventilation Requirements and Standards
Keeping indoor air clean is key to good health. HVAC systems are essential for managing ventilation systems and keeping indoor air quality high. They must follow strict rules and standards to do this well.
The air exchange rate is a big deal. It shows how often the air inside is swapped for fresh air from outside. Groups like the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) set rules for this based on the building’s use and how many people are there.
- ASHRAE Standard 62.1 sets rules for air in offices, schools, and hospitals.
- The International Mechanical Code (IMC) and local codes also have rules for air in buildings.
To make air better inside, HVAC systems need to filter air well, control humidity, and bring in outside air. New tech like demand-controlled ventilation and air sensors can make air even better. They adjust based on how many people are there and the air quality.
By following standards and using new ways to ventilate, HVAC experts can make buildings healthier. This helps people feel better and is good for the planet too.
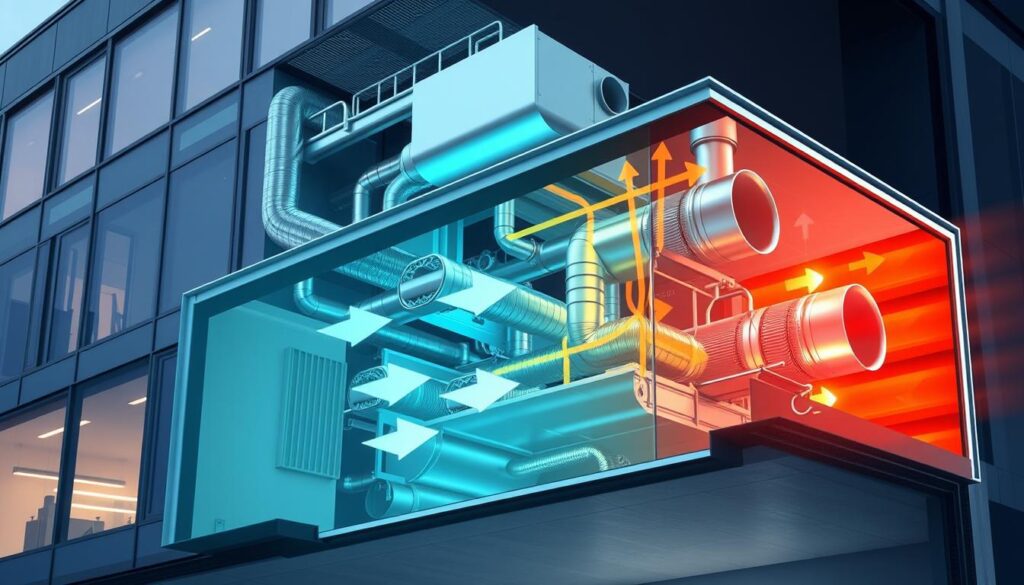
Energy Efficiency in Modern HVAC Design
Today, saving energy is key, and the HVAC industry is leading the way. It’s using smart tech, energy-saving features, and performance monitoring. These changes are changing how we heat, cool, and ventilate our spaces.
Smart Technology Integration
Smart tech has changed how we use energy in HVAC systems. Things like smart thermostats and remote monitoring help us save energy. They let us control our systems from anywhere, making sure we’re always comfortable and efficient.
Energy-Saving Features
There are many new features to make HVAC systems more efficient. High-efficiency compressors and advanced insulation are just a few examples. These features help us use less energy without losing comfort.
Performance Monitoring Systems
Performance monitoring systems are key to keeping HVAC systems running well. They track energy use and system health. This helps us catch problems early and keep our systems running at their best.
Modern HVAC design is all about saving energy and being smart. It’s making a big difference in our homes and businesses. With these new technologies, we can all do our part for the planet and save money too.
Indoor Air Quality Management
Indoor air quality should be maintained at optimum levels for you to have a healthy life.Learning about indoor air quality can make your space healthier and more comfortable.
Good ventilation is crucial for clean air. It helps remove dust, pollen, and harmful chemicals. Look for HVAC systems with advanced filters and humidity control for better air.
Temperature and humidity also matter for air quality. Too much moisture can cause mold, while dry air can hurt your breathing. Your HVAC system can help keep these levels just right.
Today’s HVAC systems also filter out outdoor pollutants. They trap harmful particles and allergens. This can help prevent respiratory problems and allergies.
By focusing on indoor air quality, you can make your space healthier. This improves your comfort, safety, and overall well-being.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
- Ensure proper ventilation through efficient HVAC systems
- Implement advanced air filtration techniques
- Maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels
- Minimize the introduction of outdoor pollutants
- Prevent and control indoor air quality problems Herr
| Indoor Air Quality Factors | Recommended Levels |
| Temperature | 68-75°F (20-24°C) |
| Relative Humidity | 30-50% |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Below 1,000 ppm |
| Particulate Matter (PM2.5) | Below 12 μg/m³ |

Future Trends in HVAC Technology
The HVAC industry is changing fast, with new tech on the horizon. We’ll see better ways to heat, cool, and ventilate our spaces. These advancements promise more energy efficiency, cleaner air, and easier system control.
Emerging Technologies
New heat recovery systems are at the forefront. They use waste heat to cut down energy use and lower bills. Solar-powered HVAC units are also gaining ground, letting us use the sun’s power for climate control.
Artificial intelligence is making HVAC systems smarter. They can now learn our preferences and adjust to save energy on the fly.
Sustainable Solutions
There’s a big push for green solutions in HVAC. Manufacturers are making eco-friendly products. These include better insulation, efficient compressors, and green refrigerants.
These green HVAC systems help the planet and save money in the long run. They’re a win-win for our environment and our wallets.
Smart Integration Advances
The future of HVAC is all about smart integration. HVAC systems will connect with smart home and building tech. This means we can control our climate, check energy use, and get alerts on our phones.
This smart tech will change how we use and manage our HVAC systems. It’s all about comfort and efficiency.
FAQ
What are the primary components of a modern HVAC system?
Modern HVAC systems have key parts like furnaces and air conditioners. They also include heat pumps, air handlers, and ductwork. Control mechanisms help them work together for comfort.
How do the different components of an HVAC system integrate to provide comprehensive climate control?
HVAC components work together for climate control. The furnace, air conditioner, and air handler regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality. This ensures a comfortable environment in buildings.
What are the scientific principles behind the heating of air in HVAC systems?
HVAC heating uses thermodynamics, heat transfer, and energy exchange. These processes change air temperature and humidity. They help achieve the desired indoor conditions.
How do heat exchange methods, such as conduction and convection, contribute to the efficiency of HVAC systems?
Conduction and convection are key to HVAC efficiency. They help in the design and performance of heating and cooling equipment. This maximizes energy use and thermal management.
What are the key considerations in designing effective air distribution systems for HVAC installations?
Good air distribution is vital for even temperature and air quality. HVAC design factors like duct layout and fan performance are important. They ensure a comfortable indoor environment.
How do refrigeration cycles work in HVAC systems, and what factors influence their efficiency?
Refrigeration cycles are crucial for air conditioning and heat pumps. They involve refrigerant compression, expansion, and evaporation. Efficiency depends on refrigerant type and system design.
What are the ventilation requirements and standards that HVAC systems must meet to ensure healthy indoor air quality?
HVAC systems need proper ventilation for air quality. They must follow industry standards for air exchange and filtration. This ensures effective contaminant removal.
How do modern HVAC systems incorporate energy-efficient features and smart technology to improve performance and reduce energy consumption?
Modern HVAC systems use energy-saving components and smart technology. These advancements improve efficiency and reduce energy use. They also offer performance monitoring.
What are the key strategies for managing indoor air quality through HVAC system design and operation?
HVAC systems are key to indoor air quality. Advanced filtration and humidity control are important. Specialized ventilation systems help reduce contaminants for healthier environments.
What are some of the emerging trends and future developments in HVAC technology that will shape the future of heating and cooling?
HVAC technology is evolving with advanced heat recovery and solar-powered units. Artificial intelligence will also play a role. These innovations aim to boost efficiency and sustainability in buildings.

1 thought on “Understanding Heating Air Technicaly: HVAC Basics Guide”